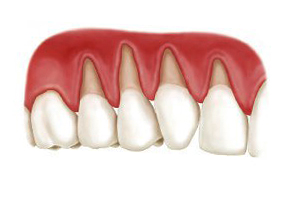
Root recession happens when your gum tissue begins to pull away from the base of your teeth to the point that it can expose the tooth roots to your oral environment. It’s a common dental problem that develops slowly, which means patients don’t typically notice it at first. When your gums recede, gaps or pockets develop between the teeth and the gum line. Bacteria collects in these pockets and causes severe oral health problems that can lead to tooth loss.
By the time you realize your gums are receding, it’s already too late to repair the damage. All you can do at that point is prevent it from getting worse. If you take certain steps, however, you can avoid it happening in the first place.
Multiple possible reasons exist for root or gum recession, such as:
Poor dental care can worsen many of these issues, with insufficient brushing, flossing and use of antibacterial mouth rinses enabling plaque to accumulate in your mouth. This turns into calculus that builds up on the teeth, which can cause gum recession.
If your gums start to recede and you don’t take urgent steps to halt the process, you’re very likely to experience bleeding, painful gums, particularly when you brush and floss your teeth. And that’s just the first stage—the long-term consequences include:
Without the gum tissue protecting your teeth from bacteria and plaque build-up, patients typically find they have an increased risk of cavities and gingivitis, and the resulting damage is more serious. Besides the health concerns caused by tooth decay, cavities and fillings are unpleasant in appearance and can affect your confidence and self-esteem.
The surface of the roots is softer than the enamel-coated parts of teeth, so exposure increases the risk of damage to the roots significantly. Grinding your teeth during sleep or brushing aggressively can cause you to lose tooth structure, and you may need restorative procedures to protect the exposed surfaces to halt the process.
Bad breath or halitosis is unpleasant at the best of times, both for you and the people you interact with. It can interfere with a relationship, and the bacteria that causes it can also affect your overall health and result in problems ranging from heart disease to kidney concerns.
A receding gum line caused by gum disease leaves a larger section of your teeth and roots exposed, making the teeth look longer than normal. It also makes stains and other discolourations more obvious, and tends to draw the eye to your mouth.
When your root becomes exposed as a result of gum recession, the tooth becomes significantly more sensitive to temperatures. This can affect your eating habits and you may no longer be able to enjoy your favourite foods and drinks.
If you notice your gums beginning to recede, visit your dentist without delay to get recommendations—before your roots become exposed.
The good news is that while receding gums cannot be reversed, the process can be halted. If it is caught early, thorough deep cleaning can remove the offending plaque. As long as you maintain your oral health regimen you can prevent it from recurring.
If the recession has already begun to affect your roots, your dentist might recommend surgical interventions such as gum tissue grafting, pocket reduction surgery, or guided bone regeneration.
A study published in the International Journal of Periodontics and Restorative Dentistry reported that the new “pinhole technique”, which involves manipulating existing gum tissue over the exposed roots, delivers a high rate of success and patient satisfaction.
Avoiding root recession from occurring or preventing it from worsening depends on a number of simple oral care procedures. Use a toothbrush with soft bristles to brush, floss and rinse twice daily, quit smoking if you haven’t already, eat a healthy, well-balanced diet, and use a night guard if you’re prone to grinding your teeth (bruxism). Get your teeth cleaned professionally twice a year and have regular dental examinations to ensure everything in your mouth is ship-shape, and receding gums will be one thing you won’t need to worry about.
For more information on treatment for receding gums or to schedule an appointment with Dr. Handler, please contact 416-267-4661.
Do you ever feel nervous about dentist appointments? Rest assured: we cater to nervous and anxious patients in a gentle and considerate manner. Call us now to schedule a free consultation!